Pediatric irritable bowel syndrome and pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: What’s the difference?

Pediatric irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are two abdomen ailments that sound the same but are distinctly different. The similarity in name and symptoms could be why these ailments are often incorrectly used interchangeably; however, it’s important to undergo an exam to come to the proper diagnosis to ensure the most suitable treatment. Here we take a look at IBS and IBD, what makes them different, how they are diagnosed, and their treatment options.
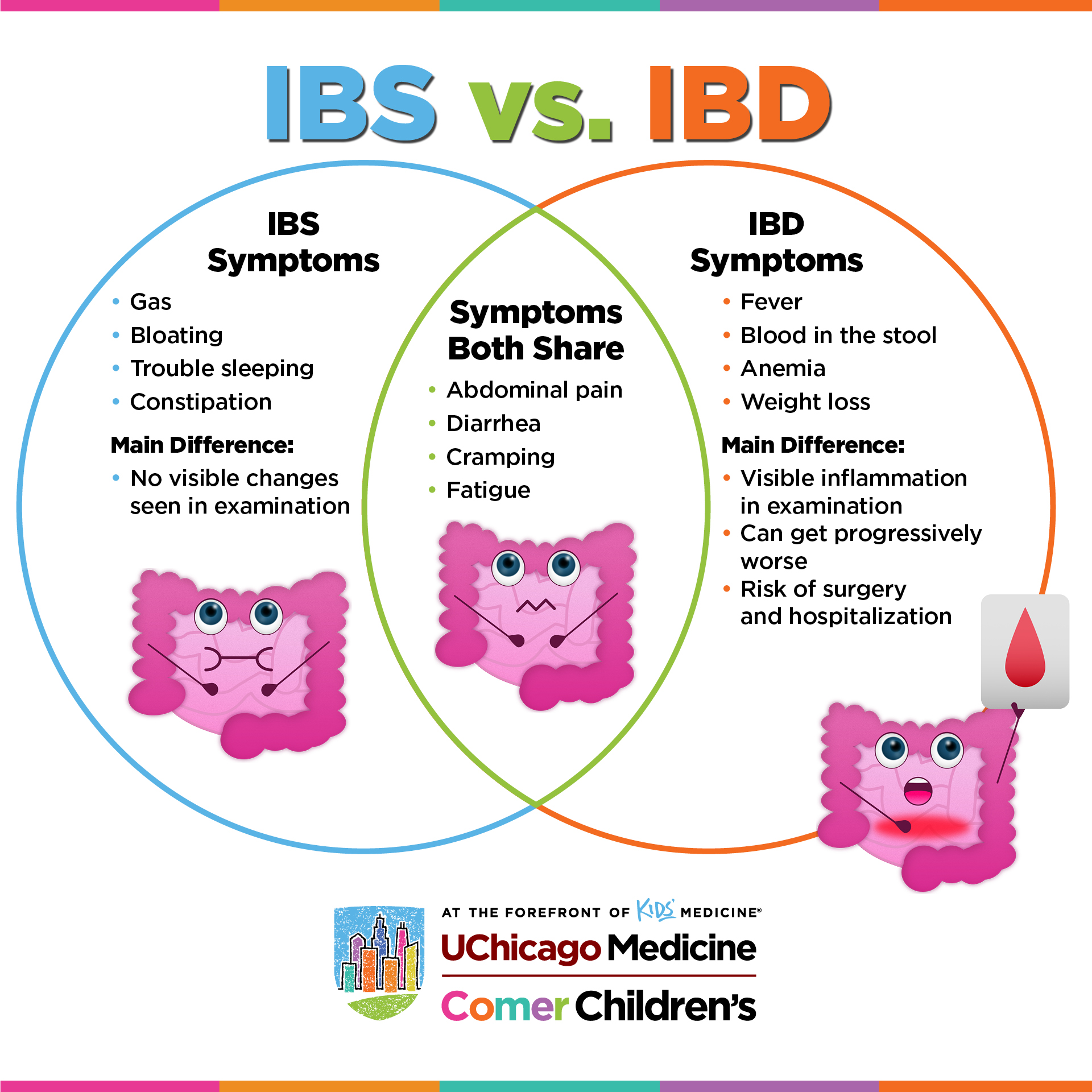
What’s the difference between pediatric IBS and pediatric IBD?
The main difference between pediatric IBS and IBD is that inflammatory bowel disease can cause destructive inflammation and permanent damage to the gastrointestinal tract, while irritable bowel syndrome does not cause inflammation and rarely requires hospitalization. Also, it’s possible for a child to have both IBS and IBD.
What causes inflammatory bowel disease in children? How is IBD diagnosed?
It is not yet known what causes inflammatory bowel disease. It is known to involve an interaction between genes, the immune system, and environmental factors, including previous gastrointestinal infection and smoke exposure. There are two main types of inflammatory bowel disease: Ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease.
Inflammatory bowel disease is caused by changes in the immune system (the system in your body that fights infection). In IBD, part of the immune system is too active and can cause inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike IBS, healthcare providers will be able to see evidence of inflammation caused by IBD through blood and stool testing as well as during an endoscopic evaluation.
Other exams used to screen for pediatric IBD include blood tests, stool studies, and imaging studies utilizing X-rays or magnetic resonance. At Comer Children’s Hospital, we are pioneering the use of intestinal ultrasound to monitor children with IBD.
Learn more about Intestinal Ultrasound for Pediatric IBD
Evaluation can also help determine if your child has ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn’s disease, two categories of IBD.
If IBD goes undiagnosed, it can lead to irreversible scarring and complications such as colon cancer. IBD can also affect other organs of the body including the eyes, skin, the joints and liver. Pediatric IBD can also cause arthritis, skin conditions, kidney issues and bone loss.
What causes irritable bowel syndrome? What are the symptoms of IBS in children?
Pediatric IBS may occur when the bowel is sensitive to specific foods or other triggers like stress. Symptoms of IBS include stomach pain and cramping, gas and bloating, trouble sleeping and fatigue, and constipation and/or diarrhea. The important thing to know is that although the symptoms can be bothersome, irritable bowel syndrome does not cause inflammation or any visible changes in the digestive tract when examined.
How are IBD and IBS treated in children?
The treatment for IBD and IBS are very different. While it’s possible to manage both IBD and IBS, there is no cure for either. Treatment options for children with irritable bowel syndrome include dietary changes and avoiding known triggers when possible. Stress management to mitigate flare ups, and medicine are also treatment options for pediatric IBS that should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Medications are necessary for the treatment of children with inflammatory bowel disease however, if the disease is severe or progresses quickly, surgery may also be necessary.
Schedule a Pediatric Gastroenterology Appointment

Schedule Online
Book a pediatric appointment online right away from the comfort of your mobile device.

Set Up A Pediatric Video Visit
Save time by skipping the trip to the doctor's office and video conference with your provider instead.

Request an Appointment
Don’t have time right now? Submit an appointment request form and we’ll call you back within two days to schedule an appointment.
